The Basics of Juvenile Periodontitis: What Every Parent Should Know

Juvenile periodontitis, also known as localized aggressive periodontitis, is a rare but severe form of periodontal disease that affects children and adolescents. It is characterized by the rapid loss of alveolar bone and attachment loss around permanent first molars and incisors, leading to loose teeth and eventual tooth loss if left untreated. The gum specialists will help restore your diseased tissues through a range of dental services in Concord, NC.
In this article, we will delve into the world of juvenile periodontitis, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
What is periodontitis?
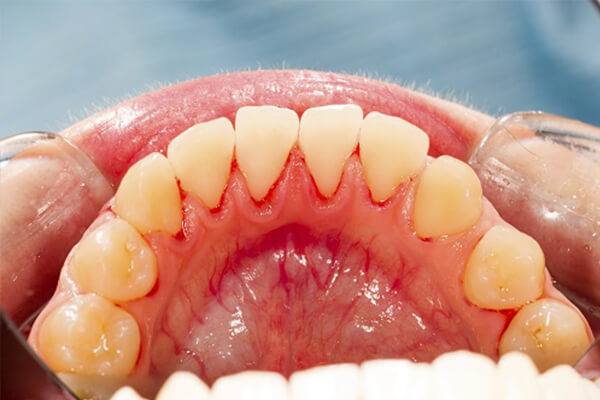
Periodontitis, gum or periodontal disease, is a severe and advanced stage of gum inflammation. It is a chronic bacterial infection that affects the tissues surrounding and supporting the teeth, including the gums, periodontal ligament, and alveolar bone.
What causes juvenile periodontitis?
Typically, plaque accumulation due to increased bacterial infiltration causes periodontitis. Failure to remove the plaque through proper hygiene practices like brushing, flossing, and regular dental cleanings may harden into calculus, which allows bacteria to thrive. As the bacteria grow, they produce toxins and acids that irritate your gums leading to inflammation (gingivitis), which may progress to periodontitis.
The following factors may contribute to the development of juvenile periodontitis:
-
Genetic predisposition
-
-
- Having a family member with periodontal disease due to improper immune response
-
-
Poor oral hygiene
-
-
- Improper brushing and flossing can result in increased plaque accumulation and bacterial colonization.
-
-
Impaired immune response
-
-
- Children with compromised immune systems or having any underlying medical condition like juvenile diabetes or anemia may be more susceptible to periodontitis.
- An impaired immune system makes it harder for the body to fight off infections and control inflammation.
-
-
Other factors
-
- Poor nutrition and puberty may be other factors that contribute to the progression of these conditions.
What are the stages involved in juvenile periodontitis?
Juvenile periodontitis involves the following stages:
- Stage I: There is degeneration of principal fibers of the periodontal ligament with alveolar bone resorption
- Stage II: There is rapid proliferation of epithelial cells along the root, which exhibits the earliest signs of inflammation
- Stage III: There is progressive inflammation and development of deep, infrabony periodontal pockets
What are the symptoms associated with juvenile periodontitis?
The symptoms of juvenile periodontitis may include:
- Red, swollen, and bleeding gums
- Painful chewing
- Bad breath
- Formation of deep periodontal pockets
- Malocclusion (bite changes)
- Pus between the teeth and gums
- Receding gums
- Loose teeth
What are the radiographic findings of juvenile periodontitis?
Radiographically when viewed, juvenile periodontitis may exhibit the following findings:
- Vertical or angular bone loss around the first molars and incisors
- The pattern appears to be an “arch-shaped” loss of alveolar bone from premolars to molars
- Frequently bilaterally symmetrical pattern of bone loss occurs as a “mirror image pattern”.
How do dentists diagnose juvenile periodontitis?
Diagnosing juvenile periodontitis involves recording the symptoms and medical history. History helps rule out the possibility of genetic risk, and other medical conditions indicating a compromised immune system. This is followed by a comprehensive dental examination, including:
- Visual examination of the teeth and gums
- Periodontal probing to measure pocket depth
- X-rays to assess bone loss
- Bacterial testing to identify periodontal pathogens
How is juvenile periodontitis treated?
Treatment of juvenile periodontitis typically involves a combination of:
- Scaling and root planing to remove plaque and tartar
- Antibiotics to combat bacterial infection
- Surgical procedures to repair damaged tissues
- Orthodontic treatment to improve tooth alignment
- Regular maintenance appointments to monitor progress
Can juvenile periodontitis be prevented?
With proper oral care, juvenile periodontitis can be effectively prevented through the following tips:
- Good oral hygiene practices, such as brushing and flossing
- Regular dental check-ups every once in six months
- A balanced diet low in sugar and carbohydrates
- Hydrating yourself well
- Avoiding tobacco products
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques like Yoga or meditation
Juvenile periodontitis is a serious condition that requires prompt attention and treatment. By understanding its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies, we can work together to prevent tooth loss and promote oral health in children and adolescents. If you suspect your child may be at risk or are experiencing symptoms, consult a pediatric dentist or periodontist for a comprehensive evaluation and treatment plan. Early intervention is key to saving teeth and ensuring a healthy smile for life.